World War I Versus World War II
By: Jazmin Haque
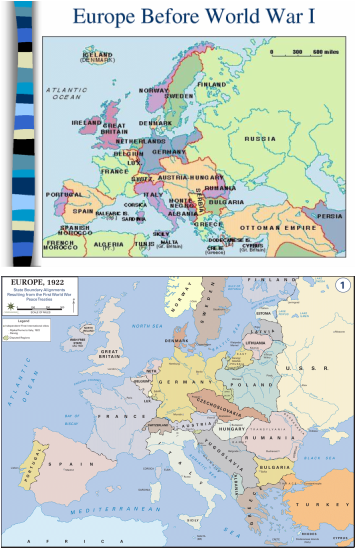
Causes of WWI & WWIIImmediate origins of the war are due to decisions of Serbia. Gavrilo Princip, a Serbian, had assassinated Archduke Francis Ferdinand, the heir to the Austria-Hungary throne on June 28, 1914. This was the first event that had caused the beginning of World War I but the origins of the war go a lot farther back and involve national politics, cultures, economics, and alliances between European powers since 1870.
It can be seen that militarism, alliances, imperialism, and nationalism had cause for much conflict that led up the World War I. At the beginning of the 20th century, an arms race had begum. Germany had been seen to have the largest increase in their military by 1949. At this time Great Britain and Germany had also increased their navies. The military establishments in Europe had also started to have a larger influence on public policies. These increases in militarism had pushed the countries into a war. Alliances had also caused for the war to begin. Many countries throughout Europe had made defense agreements that would pull them into battle to defend each other if one country was attacked. Imperialism leading up to World War I had caused for increased competition within the world. These increased powers and greater empires had led to more confrontations between nations further leading the world into the war. Lastly, nationalism had a large part in directing the war. It had caused for each country to try to prove their dominance and power, further creating more tensions between the world. WWII was really caused by the aftermath of WWI. Germany’s economy taking a turn for the world along with the rest of the world had caused for powers to be hostile and have mistrust in each other. The League of Nations had not been as successful as planned and there were many tensions between the world’s powers. After Germany had invaded Poland, rejecting Britain and France’s previous demands, World War II had started. |
Technology of WWI & WWIIWorld War I technology had reflected the period of industrialism and its weapons had been made in mass productions. Trench warfare was a new strategy that had been used during World War I and had allowed for new technologies to be used. Artillery was a technological change in this war as well. Factors such as weather and barrel wear could be taken into account while firing for the first time and the majority of casualties during the war were due to artillery fire. Another aspect of new technology used in WWI was poison gas. Germany’s advanced chemical industry had allowed for them to use it as a weapon in trench warfare. It had been used first on the battlefield in April 1915. Mustard gas and phosgene were other gases that had been used later in the war.
There had been many new technological breakthroughs during World War II. Between the wars, innovation of automatic weapons had improved tremendously. The machine gun which fired 1500 rounds per minute was developed by Germany and there had been many more automatic weapons that were developed. These innovations had allowed for these weapons to be more mobile and popular during the second world war. Planes were also a very large improvement in warfare for World War II. Planes were able to be more heavily armed and able to drop bombs. Bombings had caused many deaths during the war. Lastly, the atom bomb was the most powerful technological innovation to be used during World War II. The Manhattan Project had produced the first atomic bombs that were used to kill hundreds of thousands of people. |
Human LossesWorld War I had ended with a total number of 37 million casualties. There had been over 17 million deaths and 20 million wounded. Of those 17 million deaths, 10 million of those had been military personnel and 7 million had included civilians. It can be estimated that the Allies had lost about 6 million soldiers while the central powers had lose 4 million. The majority of deaths had been due to battle rather than diseases in the previous wars.
World War II is known as “the deadliest military conflict in history”. There had been over 60 million people killed during the world which had been 2.5% of the population at the time. It can be approximated that about 23 million of those deaths had been military deaths. About 11 million deaths had been caused by the Holocaust alone, 6 million of them being Jewish. |
Political Outcomes of the WarsThe political outcomes of World War I had included the Treaty of Versailles, the decline of European power in exchange for North American power, democratic states taking the monarchies place, and the rise of Communism and Fascism. After WWI the United States held all of the economic power and most of the world had been in debt to it. Germany’s power had been diminished due to the Treaty of Versailles. Economic consequences include the failure of Europe’s economy and eventually the Great Depression which had affected both the United States and Europe. Communism and Fascism had become more popular in Italy, Japan, and Germany due to their political states after the war.
The outcome of World War II had shown in favor of the United States. Once again, Germany had been defeated and had declined. WII had signaled the emergence of the United States as a superpower. The outcome of World War II had brought tensions between the communist and capitalist worlds. The United Nations had been created after the war as well. Europe’s power was diminished due to the damage due to the war as well as in Japan. |
Works Cited:
"Causes of World War I." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 05 Apr. 2013. Web. 05 May 2013. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Causes_of_World_War_I>.
"World War I Casualties." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 05 Apr. 2013. Web. 05 May 2013. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_War_I_casualties>.
"World War II Casualties." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 05 May 2013. Web. 05 May 2013. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_War_II_casualties>."Firstworldwar.com." First World War.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 05 May 2013. <http://www.firstworldwar.com/features/womenww1_three.htm>.
"Imperial Japan." - World War 2 on History. N.p., n.d. Web. 05 May 2013. <http://www.history.co.uk/explore-history/ww2/imperial-japan.html>.
"Causes Of World War 1" American History.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 05 May 2013. <http://americanhistory.about.com/od/worldwari/tp/causes-of-world-war-1.htm>.
"Causes of World War I." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 05 Apr. 2013. Web. 05 May 2013. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Causes_of_World_War_I>.
"World War I Casualties." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 05 Apr. 2013. Web. 05 May 2013. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_War_I_casualties>.
"World War II Casualties." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 05 May 2013. Web. 05 May 2013. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_War_II_casualties>."Firstworldwar.com." First World War.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 05 May 2013. <http://www.firstworldwar.com/features/womenww1_three.htm>.
"Imperial Japan." - World War 2 on History. N.p., n.d. Web. 05 May 2013. <http://www.history.co.uk/explore-history/ww2/imperial-japan.html>.
"Causes Of World War 1" American History.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 05 May 2013. <http://americanhistory.about.com/od/worldwari/tp/causes-of-world-war-1.htm>.