Christianity
By: Elodie Chidiac
"For God so loved the world that he gave his one and only Son, that whoever believes in him shall not perish but have eternal life." John 3:16
Christians believe that Jesus, Son of God, was sent to earth to save all human beings and offer eternal life to whoever followed him.
Geography
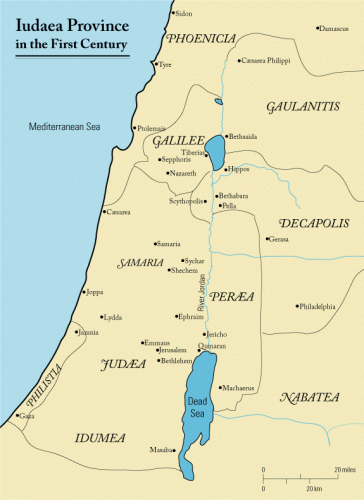
Originally a small group of Jews practiced the religion, but Christianity quickly expanded into the non-Jewish community and throughout the Roman Empire more specifically the Roman State of Judea.
Originally a small group of Jews practiced the religion, but Christianity quickly expanded into the non-Jewish community and throughout the Roman Empire more specifically the Roman State of Judea.
History
Christianity came into existence with Jesus of Nazareth, a Jewish teacher who claimed to be the Son of God, the Messiah, for whom the Jewish had long awaited. Many people followed his teachings about devotion and love for other human beings. Jesus was known for using parables that were earthly stories with a heavenly meaning.
The Romans and the Jewish Pharisees (priests) rebelled and in 30 C.E. Jesus was crucified. His followers believed that he rose from the dead and ascended into heaven. Thus Christians deem in the resurrection of Jesus Christ who is both human and divine.
Christianity came into existence with Jesus of Nazareth, a Jewish teacher who claimed to be the Son of God, the Messiah, for whom the Jewish had long awaited. Many people followed his teachings about devotion and love for other human beings. Jesus was known for using parables that were earthly stories with a heavenly meaning.
The Romans and the Jewish Pharisees (priests) rebelled and in 30 C.E. Jesus was crucified. His followers believed that he rose from the dead and ascended into heaven. Thus Christians deem in the resurrection of Jesus Christ who is both human and divine.
Religious Text: The Bible
Christianity is based on both the Old and New Testaments of the Bible. The Old Testament described the history of the people that God choose to be the ones through whom the Messiah would come. Therefore, it contains the history of God's people, the Jews. The New Testament was written later as a demonstration of the fulfillment of the Old Testament Prophecies of Jesus.
Values and Beliefs
Christians believe that Jesus Christ is the Son of God and that the forgiveness of sins, and everlasting life, is achievable only through belief in divinity, death and resurrection of Christ.Jesus acted as the link between God and human beings. They view that man was made on the Sabbath day by a sovereign God who was the creator of all things and matter.
Christians are expected to know God, to worship him, and to practice love and service him and other human beings. They tend to follow the ten commandments that were given to Moses, the prophet who freed the Jews from Egypt.
Christians believe that Jesus Christ is the Son of God and that the forgiveness of sins, and everlasting life, is achievable only through belief in divinity, death and resurrection of Christ.Jesus acted as the link between God and human beings. They view that man was made on the Sabbath day by a sovereign God who was the creator of all things and matter.
Christians are expected to know God, to worship him, and to practice love and service him and other human beings. They tend to follow the ten commandments that were given to Moses, the prophet who freed the Jews from Egypt.
Worldwide impact
In the early days, Christianity was spread by Paul the Tarsus and the twelve disciples who were chosen by Jesus. Paul was an anti-Christian at first who was converted by a vision of Christ and thus spread Jesus' teachings.
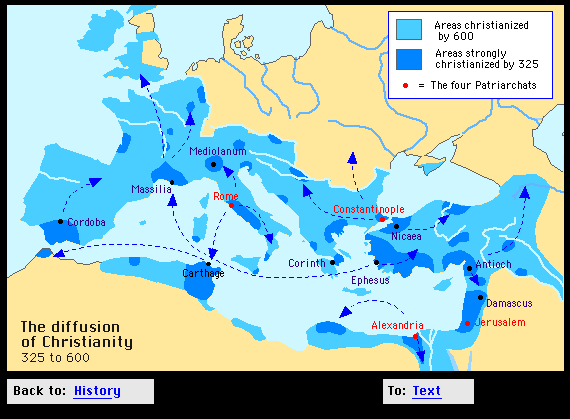
By the third century C.E, Christianity had become the most powerful religion in the Mediterranean basin. It was eventually adopted by Constantine after he claimed having a vision of Christ while on the battlefield. Later, it was made the official religion by Theodosius since the use of religious code of laws helped unify the people. Eventually, Christianity branched out westward and northward into regions beyond the boundaries of the Roman Empire.
In the early days, Christianity was spread by Paul the Tarsus and the twelve disciples who were chosen by Jesus. Paul was an anti-Christian at first who was converted by a vision of Christ and thus spread Jesus' teachings.
By the third century C.E, Christianity had become the most powerful religion in the Mediterranean basin. It was eventually adopted by Constantine after he claimed having a vision of Christ while on the battlefield. Later, it was made the official religion by Theodosius since the use of religious code of laws helped unify the people. Eventually, Christianity branched out westward and northward into regions beyond the boundaries of the Roman Empire.
The Formation of Modern Christianity
Augustine was one of the foremost philosopher of early Christianity and the leading figure of the church of North Africa. He questioned contemporary religions more specifically Christianity. Augustine's philosophy was always concrete, derived from his own personal experiences. According to him, Christianity was the true philosophy. Truth is one, and God is truth. Augustine stood strong behind his beliefs arguing that only faith provides the base from which the quest for wisdom starts. He published writings such as Confessions to make Christianity more intellectually appealing. Later, Augustine began the process of establishing an official doctrine which was emphasized by Constantine to unite the Empire. Looking at different texts and philosophies, Augustine drew the conclusion that Jesus was both divine and human. He, then, created a church hierarchy that consists of five bishops: Jerusalem, Antioch, Alexandria, Constantinople and Rome which was the most powerful of all.
Augustine was one of the foremost philosopher of early Christianity and the leading figure of the church of North Africa. He questioned contemporary religions more specifically Christianity. Augustine's philosophy was always concrete, derived from his own personal experiences. According to him, Christianity was the true philosophy. Truth is one, and God is truth. Augustine stood strong behind his beliefs arguing that only faith provides the base from which the quest for wisdom starts. He published writings such as Confessions to make Christianity more intellectually appealing. Later, Augustine began the process of establishing an official doctrine which was emphasized by Constantine to unite the Empire. Looking at different texts and philosophies, Augustine drew the conclusion that Jesus was both divine and human. He, then, created a church hierarchy that consists of five bishops: Jerusalem, Antioch, Alexandria, Constantinople and Rome which was the most powerful of all.
Gender Roles
Mary Magdalene's story is intimately linked with Jesus. She plays a starring role in one of the most powerful and important scenes in the Gospels. When Jesus was crucified, Mary Magdalene was supporting him in his final terrifying moments. She was also the one who discovered the empty tomb and was the first witness of Jesus' resurrection. Although Mary Magdalene first image in the Bible is portrayed as a prostitute and thus a sinner, she plays a major role in the Christian faith when she washes Jesus's feet with tears and wipe them with her own hair, and kissed his feet and anointed them with ointment. She has fallen but was redeemed, and thus she portrays an imagine of redemption, a signal that no matter how low one falls, one can be redeemed and Jesus will forgive one's sins. Mary Magdalene was one of the most devoted followers of Jesus Christ and is considered a saint in the Christian faith.
In both Buddhism and Christianity, women were considered equal in their ability to achieve salvation or nirvana comparing to India where women could not achieve Moksha. Also, in both religions women were allowed to remove themselves from traditional roles and become nuns living in convents away from society. Within the various Christian traditions both men and women can be recalled as saints.
Mary Magdalene's story is intimately linked with Jesus. She plays a starring role in one of the most powerful and important scenes in the Gospels. When Jesus was crucified, Mary Magdalene was supporting him in his final terrifying moments. She was also the one who discovered the empty tomb and was the first witness of Jesus' resurrection. Although Mary Magdalene first image in the Bible is portrayed as a prostitute and thus a sinner, she plays a major role in the Christian faith when she washes Jesus's feet with tears and wipe them with her own hair, and kissed his feet and anointed them with ointment. She has fallen but was redeemed, and thus she portrays an imagine of redemption, a signal that no matter how low one falls, one can be redeemed and Jesus will forgive one's sins. Mary Magdalene was one of the most devoted followers of Jesus Christ and is considered a saint in the Christian faith.
In both Buddhism and Christianity, women were considered equal in their ability to achieve salvation or nirvana comparing to India where women could not achieve Moksha. Also, in both religions women were allowed to remove themselves from traditional roles and become nuns living in convents away from society. Within the various Christian traditions both men and women can be recalled as saints.
Citations
"Why Is the Bible Divided into Two Parts: The Old Testament and The New Testament."CARM. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Nov. 2012. <http://carm.org/bible-two-parts>.
Armstrong, Monty. "6." Cracking the AP World History Exam. New York: Random House, 2012. N. pag. Print
"Gender Roles in Christianity." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 11 Mar. 2012. Web. 08 Nov. 2012. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gender_roles_in_Christianity>.
"Religious Symbols Meaning." Religious Symbols. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Nov. 2012"Your Browser Is No Longer Supported." Google AdWords. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Nov. 2012. <https://adwords.google.com/select/KeywordToolExternal>."Pedro M. Rosario Barbosa's Blog." Pedro M. Rosario Barbosa's Blog. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Nov. 2012. <http://pmrb.net/blog/tag/paul-of-tarsus/>."World History : HyperHistory." World History : HyperHistory. N.p., n.d. Web. 09 Nov. 2012. <http://www.hyperhistory.com/online_n2/History_n2/a.html>.BBC News. BBC, n.d. Web. 18 Nov. 2012. <http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/christianity/history/marymagdalene.shtml>.
"Why Is the Bible Divided into Two Parts: The Old Testament and The New Testament."CARM. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Nov. 2012. <http://carm.org/bible-two-parts>.
Armstrong, Monty. "6." Cracking the AP World History Exam. New York: Random House, 2012. N. pag. Print
"Gender Roles in Christianity." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 11 Mar. 2012. Web. 08 Nov. 2012. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gender_roles_in_Christianity>.
"Religious Symbols Meaning." Religious Symbols. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Nov. 2012"Your Browser Is No Longer Supported." Google AdWords. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Nov. 2012. <https://adwords.google.com/select/KeywordToolExternal>."Pedro M. Rosario Barbosa's Blog." Pedro M. Rosario Barbosa's Blog. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Nov. 2012. <http://pmrb.net/blog/tag/paul-of-tarsus/>."World History : HyperHistory." World History : HyperHistory. N.p., n.d. Web. 09 Nov. 2012. <http://www.hyperhistory.com/online_n2/History_n2/a.html>.BBC News. BBC, n.d. Web. 18 Nov. 2012. <http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/christianity/history/marymagdalene.shtml>.