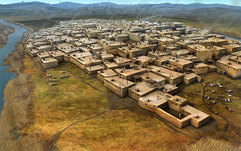
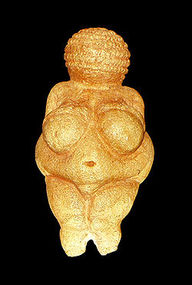
Arts and Artisanship
Paintings
|
|
Citations
Strayer, Robert W. Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources. Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martins, 2011. Print. pg 16-17"Venus Figurines."
Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 10 Apr. 2012. Web. 05 Oct. 2012. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Venus_figurines>."Nude Woman (Venus of Willendorf)."
- Smarthistory. N.p., n.d. Web. 05 Oct. 2012. <http://smarthistory.khanacademy.org/nude-woman-venus-of-willendorf.html>.
"The Oldest Art: Cave Wall Paintings." - Softpedia. N.p., n.d. Web. 05 Oct. 2012. <http://news.softpedia.com/news/The-Oldest-Art-Cave-Wall-Paintings-78754.shtml>."PaleolithicAge." Neolithic Venuses. N.p., n.d. Web. 05 Oct. 2012. <http://barclay1720.tripod.com/hist/paleo/neovenus.htm>."Neolithic Culture." Neolithic Culture. N.p., n.d. Web. 05 Oct. 2012. http://www.fhw.gr/chronos/01/en/nl/culture/weavfr.html.
Strayer, Robert W. Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources. Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martins, 2011. Print. pg 16-17"Venus Figurines."
Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 10 Apr. 2012. Web. 05 Oct. 2012. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Venus_figurines>."Nude Woman (Venus of Willendorf)."
- Smarthistory. N.p., n.d. Web. 05 Oct. 2012. <http://smarthistory.khanacademy.org/nude-woman-venus-of-willendorf.html>.
"The Oldest Art: Cave Wall Paintings." - Softpedia. N.p., n.d. Web. 05 Oct. 2012. <http://news.softpedia.com/news/The-Oldest-Art-Cave-Wall-Paintings-78754.shtml>."PaleolithicAge." Neolithic Venuses. N.p., n.d. Web. 05 Oct. 2012. <http://barclay1720.tripod.com/hist/paleo/neovenus.htm>."Neolithic Culture." Neolithic Culture. N.p., n.d. Web. 05 Oct. 2012. http://www.fhw.gr/chronos/01/en/nl/culture/weavfr.html.