AGMSPRITE
by Yazmin Gooren
Art and Architecture: People express their values through the arts, as can be seen time and time again. Daoists inspired Chinese landscape paintings, and the Greeks and Romans created beautiful, complex sculptures of the philosophers which guided their lifestyles. Christianity encouraged the building of beautiful churches and creation in Jesus's image. In this way, the wide-spread unity inspired by religion encouraged the arts to flourish.
Geography: not affected by religion.
Military: Kshatriyas were the designated warriors in Buddhist society, and it was their duty to fullfill that role dilligently.
Society: Society as a whole was impacted by religion because it was, in most cases, brought together under all-encompassing principles. Daoism and Confucianism combined to permeate Chinese culture; Christianity eventually infiltrated the Roman empire; and Greco-Roman philosophies directly involved Rome and Greece's (elite) citizens in the questioning of the self, and others.
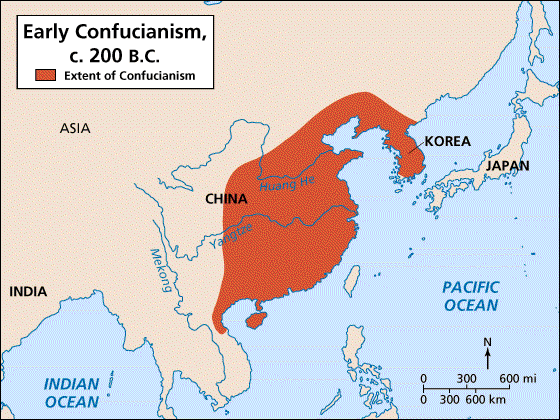
Politics: Seeing as Daoism and Confucianism were more belief systems than religions, it was these which attempted to impact politics the most by restoring order to society. The age of the "Warring States" had prevented any sort of this order from happening, and it was the Daoist response to simply retreat to nature, and abandon any sort of other pursuit. However, Confucianism took a much more direct approach, directly teaching students how to become "superior individuals" fit of serving the country's government.
Religion: see Basic Gist.
Intellect: Intellect was negatively impacted by Daoism, as it discouraged the pursuit of any sort of higher education or ambitious thought; intellect was positively impacted by Confucianism, as it actively encouraged those who wished to be "superior" to become knowledgable in all areas appropriate. Greco-Roman Philosophy impacted intellect by 1. producing a vast array of written philosophical works by its many key figures and 2. urging citizens to take a closer and often more introspective look at everyday endeavors.
Technology: Education was very highly valued by Confucianists, meaning that tools were a likely product of any intellectua innovations.
Economy: Daoism impacted the economy by discouraging people from actively pursuing professional positions, Confucianism did the opposite.
Geography: not affected by religion.
Military: Kshatriyas were the designated warriors in Buddhist society, and it was their duty to fullfill that role dilligently.
Society: Society as a whole was impacted by religion because it was, in most cases, brought together under all-encompassing principles. Daoism and Confucianism combined to permeate Chinese culture; Christianity eventually infiltrated the Roman empire; and Greco-Roman philosophies directly involved Rome and Greece's (elite) citizens in the questioning of the self, and others.
Politics: Seeing as Daoism and Confucianism were more belief systems than religions, it was these which attempted to impact politics the most by restoring order to society. The age of the "Warring States" had prevented any sort of this order from happening, and it was the Daoist response to simply retreat to nature, and abandon any sort of other pursuit. However, Confucianism took a much more direct approach, directly teaching students how to become "superior individuals" fit of serving the country's government.
Religion: see Basic Gist.
Intellect: Intellect was negatively impacted by Daoism, as it discouraged the pursuit of any sort of higher education or ambitious thought; intellect was positively impacted by Confucianism, as it actively encouraged those who wished to be "superior" to become knowledgable in all areas appropriate. Greco-Roman Philosophy impacted intellect by 1. producing a vast array of written philosophical works by its many key figures and 2. urging citizens to take a closer and often more introspective look at everyday endeavors.
Technology: Education was very highly valued by Confucianists, meaning that tools were a likely product of any intellectua innovations.
Economy: Daoism impacted the economy by discouraging people from actively pursuing professional positions, Confucianism did the opposite.
Works Cited:
Armstrong, Monty, David Daniel, Abby Kanarek, and Alexandra Freer. "Chapter 6;
Ancient Stuff: Around 8000 BCE to Around 600 CE." Cracking the AP:
World History Exam 2013. 2013 ed. New York: Random House, 2012. 118-123.
Print. The Princeton Review.
"Confucius Biography." Bio.com. A&E Networks Television, n.d. Web. 09
Nov. 2012. <http://www.biography.com/people/confucius-9254926>.
"Daoist Landscape Painting."Asian Society Org. n.d. Web. 11. Nov. 2012.< http://asiasociety.org/education/resources-schools/elementary-lesson-plans/attitudes-towards-nature-daoist-art>
"Early Confucianism Map." SMS. n.d. Web. 11. Nov. 2012. <http://webserver.sms.org/intranet/classes/history/worldhist/maps.htm>
Strayer, Robert W. Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources. Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martins, 2011.
Print.
Ancient Stuff: Around 8000 BCE to Around 600 CE." Cracking the AP:
World History Exam 2013. 2013 ed. New York: Random House, 2012. 118-123.
Print. The Princeton Review.
"Confucius Biography." Bio.com. A&E Networks Television, n.d. Web. 09
Nov. 2012. <http://www.biography.com/people/confucius-9254926>.
"Daoist Landscape Painting."Asian Society Org. n.d. Web. 11. Nov. 2012.< http://asiasociety.org/education/resources-schools/elementary-lesson-plans/attitudes-towards-nature-daoist-art>
"Early Confucianism Map." SMS. n.d. Web. 11. Nov. 2012. <http://webserver.sms.org/intranet/classes/history/worldhist/maps.htm>
Strayer, Robert W. Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources. Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martins, 2011.
Print.