AGMSPRITE
3.1.6 By Megan White and Evan Dafoe
Chinese Effects
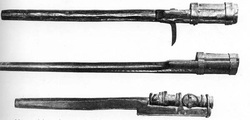
14th Century Gun
The use of gun powder allowed the Chinese to create mines and flamethrowers, creating a dramatic military advantage against other empires that used swords and bows and arrows. Gun powder caused a change in the military because the Chinese now had to be made of infantry rather than cavalry. Eventually the Chinese were able to create guns, creating an even more dramatic difference between militaries. The use of guns, mines, and flamethrowers would cause an increase in the economy. These military technologies create more deaths and casualties, thus less population. With a less population comes increased wages and standard of living. Increased wages prevent more opportunity for innovative discoveries and a stimulation in trade. Trade would continue the trend by increasing wealth even more, causing better education, sanitation, etc. China began the new way of printing, providing them with more things to trade, including ideas and technology. This would cause more wealth into the society which would allow more innovations and a higher standard of living.
India Effects

Buddhist text
India gained accessible use of printing from China, increasing their trade relations. Having an increase in trade would cause an increase in wealth for India and China alike. This stimulation of the economy would create a potential for more innovations, as well as educational benefits. The trading of printing had major effects on religion in India. Originally printing was used to copy down religious books, Buddhism in particular. After having greater technology from China, they were able to copy more religious texts. This stimulation in copying would provide more books which eventually caused Buddhism to spread. With more books comes more social benefits, such as an increase in literacy for people of all social classes instead of scribes. On the same note, previous to the adaptation of Chinese printing, India printed by carving out the individual letters. Doing so would create a higher demand for specialized artists, eventually creating an increase in art. Seeing as how religion was so stressed in India, these artists would be seen as more important on social status levels. Gunpowder caused a dramatic stimulation in trade for India. After adopting gun powder from China, they began to trade continually with China. Eventually India became the number one supplier of saltpeter to Europe. The high demand caused a great stimulation of trade in India. Combining these factors caused India to have dramatic trade relations with Europe and China, causing an increase in the economy(money) and social aspects(education). Militarily, India was far advanced with gunpowder. After creating Mysorean rockets, new innovations formed and caused India to have the "upper-hand" in military strategies. With the same idea as China, guns caused a decrease in population, higher wages, then higher educational and social benefits.
Middle East Effects

Ottoman siege of Constantinople
The vast of gunpowder in Middle Eastern empires,
like the Ottoman Empire, led to the empires western Asia to be nicknamed “Gunpowder
Empire.” The empires of this region earned this term due to their military exploits and innovations with
gunpowder weapons. The Muslim Empires of
the Middle East use of fire arms against opposing empires that would use swords
and the bow and arrow gave the Muslims a major advantage in head to head combat
and psychological warfare.These innovations
were focused primarily on fire-arms, especially in cannons and small arms. The Ottoman
conquest of the city of Constantinople required the creation of massive cannons
that were a major technological accomplishment
of the era. These cannons were able to siege an, otherwise, impenetrable fortification that had not been taken since the time of Classical Rome.
The Ottoman conquest of Constantinople was also a major religious event in history because it signified the end of the
crumbling Roman/Byzantium Empire and, as a result, the fall of Christianity throughout a large majority of the Middle East which
would not have happened without the innovation of gunpowder in Muslim Empires. The
innovation of gunpowder in the Middle East had a profound effect in the history
of the region and the development of the Islamic empires of the region.
Europe Effects

The European printing press
Like India, Europe originally wanted to use printing systems for religious texts. A difference between India and Europe though is that Europe was more focused on copying images rather than the text itself. Coping would require less artist because one could now do the work of 100s, but it also gained more wide-spread knowledge of certain images and would cause art to be a more respectable line of work. This would cause less social aggression and lead to more acceptance of specific jobs. Needing less artists though would allow for more people to experience different jobs, potentially forming more technologies. Along with the effects in China, India, and the Middle East, trade would increase the economy, causing more education reforms and leading to a more civilized society and more intellectual people.
The invention of gunpowder had a profound effect on the history of Europe. After gunpowder arrived in Europe, it was rapidly incorporated in to the military's of the continent. The invention of cannons and fire arms drastically changed warfare in Europe, making castles and heavy infantry virtually obsolete. Europeans adding water to the powder while they are making it was a major intellectual innovation as well. The addition of water to the manufacturing of gunpowder helped prevent the powder from exploding while it was being created saving countless lives in the processes. European governments also found ways to use gunpowder in public works as well. Gunpowder was used in the digging of mines which helped greatly stimulate European economies because the more mining done lead to the excavation of more gold and silver which created more wealth in the society. Gunpowder also helped alter the geography of Europe because it created cave and caused land slides that would not have existed without human intervention with gunpowder.
The invention of gunpowder had a profound effect on the history of Europe. After gunpowder arrived in Europe, it was rapidly incorporated in to the military's of the continent. The invention of cannons and fire arms drastically changed warfare in Europe, making castles and heavy infantry virtually obsolete. Europeans adding water to the powder while they are making it was a major intellectual innovation as well. The addition of water to the manufacturing of gunpowder helped prevent the powder from exploding while it was being created saving countless lives in the processes. European governments also found ways to use gunpowder in public works as well. Gunpowder was used in the digging of mines which helped greatly stimulate European economies because the more mining done lead to the excavation of more gold and silver which created more wealth in the society. Gunpowder also helped alter the geography of Europe because it created cave and caused land slides that would not have existed without human intervention with gunpowder.
Bibliography
"History of Gunpowder." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 19 Dec. 2012. Web. 20 Dec. 2012.
"Gunpowder." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 18 Dec. 2012. Web. 20 Dec. 2012.
"The Gunpowder Empires." Notes on the Gunpowder Empires. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Dec. 2012.
Grant, R. G. "Firearms and Fleets." Battle: A Visual Journey through 5,000 Years of Combat. New York: DK Pub., 2005. N. pag. Print.
"The Gunpowder Empires." Notes on the Gunpowder Empires. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Dec. 2012.
"European Kingdoms." Kingdoms of Greece. N.p., 02 Jan. 1999. Web. 20 Dec. 2012.
"Istanbul." The Conquest of Constantinople 1453. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Dec. 2012.
"End of Europe's Middle Ages - The Impact of the Printing Press." End of Europe's Middle Ages - The Impact of the Printing Press. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Dec. 2012.
"Gunpowder." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 18 Dec. 2012. Web. 20 Dec. 2012.
"The Gunpowder Empires." Notes on the Gunpowder Empires. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Dec. 2012.
Grant, R. G. "Firearms and Fleets." Battle: A Visual Journey through 5,000 Years of Combat. New York: DK Pub., 2005. N. pag. Print.
"The Gunpowder Empires." Notes on the Gunpowder Empires. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Dec. 2012.
"European Kingdoms." Kingdoms of Greece. N.p., 02 Jan. 1999. Web. 20 Dec. 2012.
"Istanbul." The Conquest of Constantinople 1453. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Dec. 2012.
"End of Europe's Middle Ages - The Impact of the Printing Press." End of Europe's Middle Ages - The Impact of the Printing Press. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Dec. 2012.
