Case Study of the Effects of the Rise and Fall of Communism
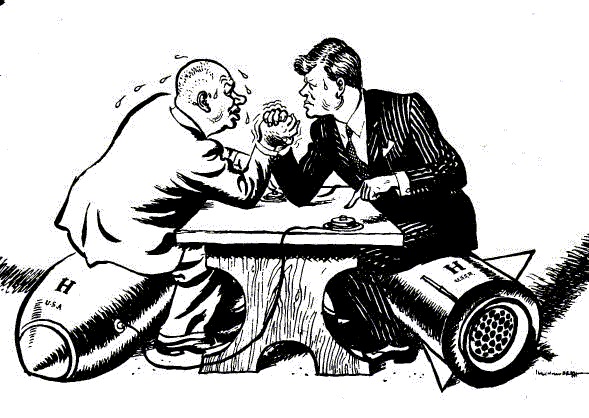
By Megan White
The Rise of CommunismTriggered in World War II, the capitalist nations were firmly against communism. Many feared the Domino Effect, where neighboring countries to communist nations would also fall to communism. In order to prevent communist nations from existing or spreading, Britain, France, and the United States put nearly all their resources, including money and military, into stopping communism. Due to these expenses, the United States eventually ran into the most significant event in their history: The Great Depression. An estimated 12,850,000 people were out of work in the United States alone. Because the United States was a global power at the time and one of the biggest allegiances to trade with, many other countries fell into economic turmoil as well. Even during these harsh times, the capitalist nations still refused to let communist spread. Referred to as the Cold War, communist and capitalist nations, particularly the Soviet Union vs. the United States, suffered great tensions. Many countries had missiles pointed at one another and nearly the entire world formed allegiances with one side of the spectrum or the other. In order to gain allegiances, countries began using military force and persuasion, regardless of if that country believed in the government they were attempting to institute. The capitalist allegiances belonged to NATO, including Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom and the United States. The communist nations formed the Warsaw Pact, including Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, Romania, the Soviet Union, and Albania. NATO and the Warsaw Pact had similar goals. By belonging to it, you assured that your country would support its fellow countries if attacked. For instance, if the United States attacked East Germany, the Soviet Union ensured that it would join the battle and provide East Germany with supplies, military, etc. Since so many nations were involved and one invasion practically guaranteed another World War, no violence ever took place.
Effects on Korea and VietnamCommunism essentially caused the division of North and South Korea along the 38th parallel. The North was invaded and supported by communist China whereas the South was supported by the democratic United States. The outcome of the Korean War ended in a cease fire with a demilitarized zone along the 38th parallel. No progress was made. North Korea, run by Kim Jong Il, was completely cut-off and isolated from the outside world. South Korea, on the other hand, is filled with diversity, freedom, and opportunity. Even art in North Korea was affected. For the few outsiders that have entered the country, all have commented on how strange it is that pictures of Kim Jong Il are plastered all over the country, even in homes. Simple family photographs aren't even on display. In comparison, communism also caused a war in Vietnam. The Vietnam War was the first war to have actual footage broadcasted across the world. Many people began opposing the war once realizing how brutal and tragic war actually was, especially because many believed Vietnam was unnecessary. In America, the first draft was instituted, sending healthy men ages 18-26 years of age into battle. This triggered widespread protests throughout the country causing many to critique the government's military motives. As shown in Figure 3, communism had a lasting impact on Korea. North Korea is still a communist nation and is unable to innovate equitably to the rest of the world. In comparison, the capitalist South Korea is filled with lights and buildings whereas the communist North is filled with darkness.
Effects on the United StatesCommunism triggered a wide-spread fear in the United States known as the Red Scare. Being led by Joseph McCarthy, the government set-out to find any communists in the United States and either imprison, kill, or banish any communist individuals. Known as McCarthyism, there was no need for evidence to accuse individuals of being communist. Shown in the American propaganda in Figure 4, Americans were terrified of what communism would do to their nation and this propaganda evoked additional fear and gave Americans reason to hate communist nations. In the propaganda, the American flag, a symbol of the country, is being burned while innocent people are being beaten and choked by communist government officials, conveying the chaos that will come from a communist government in America.
Effects on CubaCuba began as a capitalist nation with the United States as a heavy trade partner and ally. However, after Fidel Castro took control of Cuba in the 1950s, he destroyed the capitalism in the country and drifted to a communist form of government. Shortly after, Cuba, now backed by the Soviet Union, was able to create nuclear missiles and point them at the United States. In this action, known as the Cuban Missile Crisis, the United States was forced to revolt against Cuba and the Soviet Union. Although no missiles were ever fired, there were multiple attempts for the United States to kill Castro and regain Cuba as a capitalist nation, such as the Bay of Pigs. Eventually the Soviet Union collapsed causing Cuba to loose all of their finances. Since then, Cuba has remained a communist nation filled with poverty. In addition, a law in the United States was passed preventing any American citizens from travelling to Cuba unless the government granted the individual permission, such as a cultural experience. On a side note, many Americans have dodged this law by flying to Cuba out of Canada.
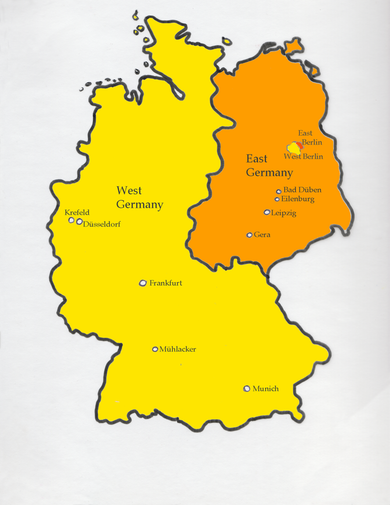
Effects on EuropeEurope was completely divided with some countries communist and some capitalist. Germany, for instance, was split in half, as shown in Figure 7. East Germany was controlled by the fascist government while West Germany was granted all freedoms. The capital of Germany, Berlin, was split in half. East Germans were not allowed to leave the country. Many found ways out, such as digging tunnels or attempted to cross mine fields and electric fences, but few were successful. Many were killed on sight. The Western part of Germany was the ideal place to live. Aside from their freedoms, they were also well nourished. East Germans were lacking health care and food, which is one thing that triggered the Berlin Airlift sponsored by America. A significant day for all Germans, and perhaps everyone in the world, is November 9th, 1989, the day the Berlin Wall was destroyed. The toppling of the Berlin Wall signified an end to communism and also demonstrated the strength of America. Some territories were finally able to form their own country, such as Poland. In 1999, Poland joined NATO and a few years later, they were able to join the European Union (2004). However, even with the fascist government gone, Europe still faces many turmoils. After being split and isolated for many years, there was a huge lack of innovations which eventually caused revolts across the continent. Even though the end of communism was seen as a positive thing, it caused desperation in many countries. Many had to rebuild their entire governments which caused more lack of innovations because they were so focused on what type of government should run the country and who should run it, since many were afraid of another Hitler or Stalin from taking control. Germany in particular faced the most hardships because they were still required to pay off the reparation from WWI, which wasn't fully paid off until 2010. With such payments, lack of innovations, and governmental questions, Europe was set behind in the global world.
|
|