THE BASIC GIST
The Colombian Exchange
was a dramatically widespread exchange of animals, plants, culture, human populations (including slaves), communicable disease, and ideas between the American and Afro-Eurasian Hemispheres following the voyage to the Americas by Christopher Columbus in 1492.
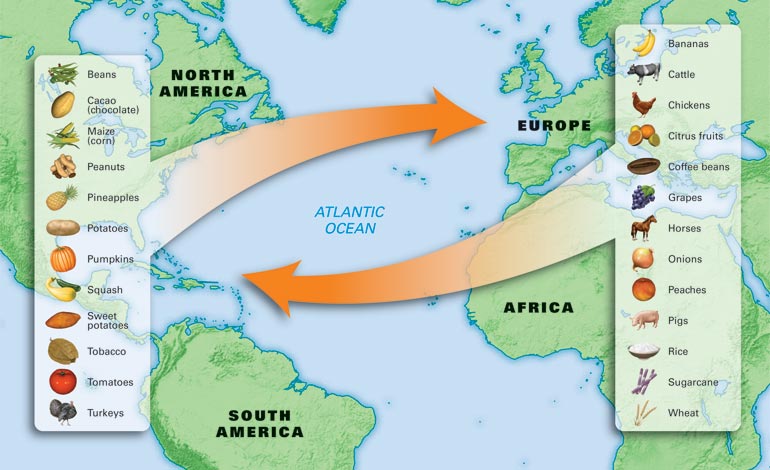
The exchange of food.
The Colombian exchange opened up new lands for the crops that were exchanged between the different cultures. Food that was displaced by the Colombian exchange were pineapples, maize, potatoes, oranges, bananas tomatoes, and chili peppers. This displacement allowed for tomatoes to be added to the diets of Italians and potatoes to be grown in Ireland so much that a shortage later caused a famine in the 1840's. This exchange of food was a way for cultural diffusion to occur across large distances and helped to form many of the stereotypical foods we have today. The tobacco crop also changed Europe creating a boom in their economy and changing the culture for the foreseeable future. Crops were not only taken from the Americas, but also brought there by Easterners; Wheat, barley, rye and sugar were all introduced to the west. Many domesticated animals were also brought from the east including the cow, horse, sheep, pig and goat. These provided beasts of burden for the people in the Americas to grow the new crops that had been brought over in much larger quantities than the natives were used to.
The exchange of goods and technology
The Columbian Exchange allowed a great deal of innovation to happen across the entire world. Before this system of trade there were no efficient means of trading across the ocean. Regions were typically isolated to their own resources, unable to experiment, innovate, or use the region's resources. With the Columbian Exchange new resources landed in every region and made innovation and efficiency much higher as well as boosting the entire world economy. The New World brought to the old world Quanine, which was the only treatment for Malaria at the time. This had a massive impact in Europe and saved many lives. African rubber being exchanged is even called a revolution by some. It was rarely used in Africa, but the Native Americans tinkered with it and found ways to use it. The rubber was used to create a wide range of items that were of central importance in their daily lives: hoods, boots, tents, balls, torches, jars, containers, syringes, toys, breastplates, rubber-headed drum sticks, and adhesives. The Natives would make these and sell them to Europe too as well as keep them for themselves. Europe would also sell these back to Africa, showing the exchange go full circle. The biggest impact was that of domesticated animals from the Old World going to the New World. Not only did these bring over pathogens that killed many, but also provided a new area of agriculture in the future. Animals changed the lives of the Natives greatly, while at first they seemed like a positive, in the end they ended up being one of the reasons for their downfall.
The exchange of ideas
The major ideas brought from the old world to the new world are: the concept of corporate structure, as well as religion (specifically Christianity). The idea of corporate structure was brought over to the Americas by trading companies such as the Dutch West India co. and the British East Indie co. This corporate structure was the first sense of complex and developed business seen in the Americas; it provided a conceptual idea that would help the Americas become a successful business hub in the future. The idea that had the largest and fastest impact was the spread of Christianity. Before the spread of Christianity, the Americas lacked a unified religion and in many cases were Polytheistic. During the Colombian exchange many missionaries would accompany traders to spread the word of Christianity, as well as many slaves would be converted by the Europeans. This effect can be seen today with the major religion from North to South America being Christianity.
Proliferation of disease
Many diseases were spread to the new and old worlds from the Colombian exchange. In the New world many of the farm animal based diseases such as smallpox, influenza and measles spread as epidemics among native people because they did not have any domesticated animals that were used in great excess to give the a chance to build up immunity's to these diseases. In fact smallpox was the largest killer of the Native Americans, even deadlier that the Black Plague of Europe. As people died of these diseases the ecosystems of the animals began to be thrown into disarray because previously hunted animals were suddenly left alone. These epidemics also caused a labor shortage in the Americas with less natives to be used as a labor force by conquerors. This was the reason African slaves were brought in, who also were carrying diseases such as malaria and yellow fever which further plagued the natives. There was not much of a flow of disease in the opposite direction though. There are sporadic causes of tuberculosis and syphilis reported, many are still unsure and evidence is not conclusive if any diseases were sent from the New world To the Old world.
Works Cited
http://public.gettysburg.edu/~tshannon/hist106web/site19/index.html
http://nationalhumanitiescenter.org/tserve/nattrans/ntecoindian/essays/columbian.htm
http://www.gilderlehrman.org/history-by-era/american-indians/essays/columbian-exchange
http://www.learnnc.org/lp/editions/nchist-twoworlds/1866http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Columbian_Exchange
http://nationalhumanitiescenter.org/tserve/nattrans/ntecoindian/essays/columbian.htm
http://www.gilderlehrman.org/history-by-era/american-indians/essays/columbian-exchange
http://www.learnnc.org/lp/editions/nchist-twoworlds/1866http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Columbian_Exchange