AGMSPRITE
4.2.3 By Mishka Wildemaan and Megan White
Art
Art was very basic, mainly stone and wood carvings. These crude forms of art suggest a lack of time to expand artistic values and ideas, most likely because they had more important tasks to complete. This shows that they were underdeveloped cultures, because their free time was taken up with fighting and finding recources to survive.
|
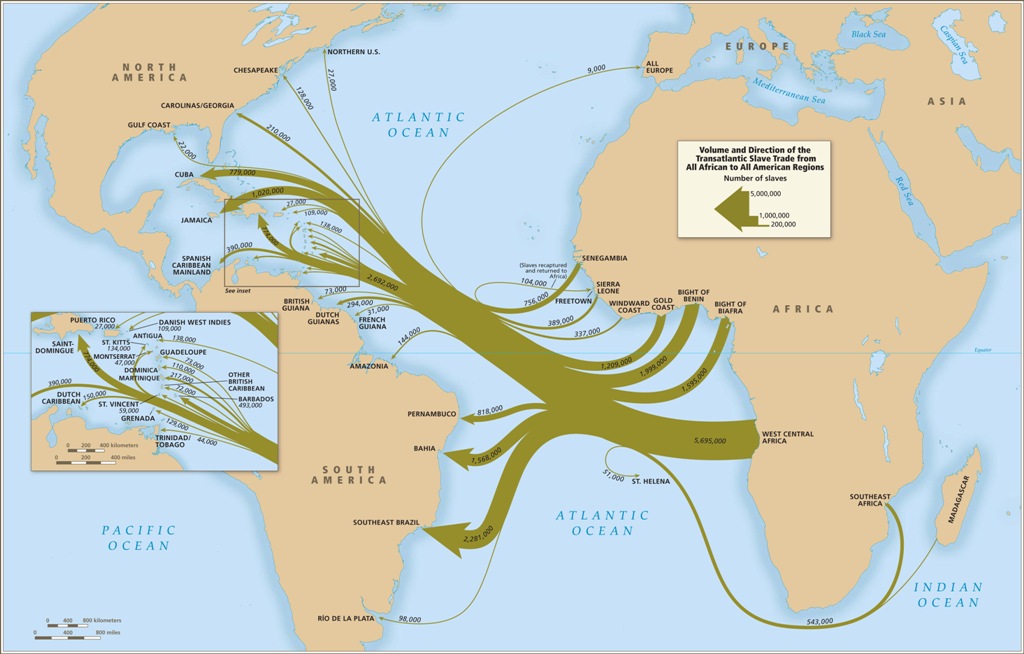
GeographyThe geography of the slave trade was mostly confined to the Western coast of Africa, and slaves were brought to the Eastern coast of the Americas. However, the slaves themselves came from all across Africa due to the nature of the trades, where chiefs would fight with other villages and claim prisoners to sell to Europeans. South America had a much higher import rate due to the fact that they would free their slaves after a certain amount of work, which led to a near-constant need for more slaves. Northern America, however, had a much lower import ratio due to their slave policies, which would usually include slavery for life and enslavement of children born there. In long term, the trade routes affected geography because they kept the African continent broken into separate political states due to the rivalry of capturing slaves.
|
MilitaryIn Africa, the fractured tribes began acquiring guns through the European trade in order to protect their own people from being kidnapped into slavery. However, with a smaller population came a smaller amount of people able to dedicate their time to the military, making it even harder to protect themselves from enemy tribes. In the Americas, however, their military was able to grow due to the surplus of labor and population. In Africa, they fought against each other to gain slaves yet didn't develop their own military technologies, causing the European guns to be more appealing and continuing the high demand for slaves.
|
SocialSlavery has had a vast social influence on all parts of society and has impacted many significant parts of it. Slavery's major impact was feelings of racism towards blacks, which led to a host of smaller issues, such as discrimination and stereotyping. Blacks were commonly discriminated against, including free ones, who were sometimes even captured and sold back into slavery. It also led to social rights issues, such as how to count slaves when doing a census count or if they were allowed to vote. The Trans-Saharan slave trade caused more divisions between African tribes due to kidnappings of men, women, and children of other tribes.
|
PoliticalIn the Americas, politicians soon disagreed on many things due to the different viewpoints toward slavery. As an example, the South attempted to pass the "Three-Fifths Compromise", saying that each slave should serve as a 3/5 of a person, allowing them more say in the House of Representatives and distribution of taxes. Although it eventually passed, the North felt that only free slaves in states should be counted towards the population, seeing as how the South didn't view slaves as people anyways. The governments in Africa were corrupted because of trying to get more slaves from other tribes, creating more political rivalry between the different states.
|
ReligionThe Europeans had viewed previously practiced African religions as satanic and would whip those caught practicing their faith. This brutal punishment caused a decrease in Africans practicing their religions because they were scared of what might happen if caught. On the other hand, Africans who were too passionate about their religions to give up the faith began having secret rituals, causing them to learn how to sneak around their European owners.
|
IntellectualAfricans in the Americas soon plummeted intellectually due to the outlawing of slaves allowing them to learn, own books, read or write, or even white men attempting to teach them. If found with possession of a book, they were be brutally beaten or worse lynched. Although some exceptions managed to learn behind the whites' back, the "rule" was that most Africans were uneducated, including illiteracy/ Once slavery had been outlawed and the blacks were free, some did not know how to conform to the ways of society. Many actually returned to their owners asking for jobs because working the fields is all they had ever known to do. In regards to the African continent, much of their intellect was sent over to the Americas and droned into only knowing how to work as a slave, robbing Africa of their potential doctors, scientists, etc. creating less intellect for the continent as a whole.
|
TechnologyWith a surplus labor force, Europeans living in the Americas began experimenting with ways for slavery to be even more efficient. The greed of having less slaves but more products to sell eventually led to the inventions of the cotton gin and advanced plows, yet most of the slaves still worked by hand.
|
EconomySlavery had an overall poor effect on the economy, because there were large amounts of people not recieving pay for their work. This meant that the slaves, while acting as workers, could not fulfill their role as consumers. When people are working and not buying, those selling have less financial gain, and the cycle continues. Another reason why slavery negatively affected the economy is that the slaves, recieving no compensation for their work, had little reason to work as hard as possible. Slaves would routinely feign illness, damage crops, or otherwise shirk their duties, because of their poor treatment. This is doubtlessly something they would not have done if they were recieving reward for their work. These reasons all lead to inferior goods, as well as less innovation and work ethic. Both of those negatively affected the economy.
|
Citations
"Economic Impact of Slavery and Emancipation in America." - Dickinson College
Wiki. N.p., 27 Dec. 2007. Web. 07 Feb. 2013.
Cassie Jones." History100slaverys Blog. N.p., n.d. Web. 07 Feb. 2013.
rans-Saharan Trade." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 02 Apr. 2013. Web. 07 Feb. 2013.
"The
Interesting Narrative of the Life of Olaudah Equiano, or Gustavus Vassa, the African. Written by
Himself. Vol. I." Documenting the American South. N.p., n.d. Web.
<http://docsouth.unc.edu/neh/equiano1/summary.html>.
"European
Exploration and Colonization, Page 13." American History. N.p., n.d. Web. 07 Feb. 2013. <http://aventalearning.com/content168staging/2008AmHistA/unit1/html/section_4_page_13.html>.
"Medicine through Time - Smallpox." Smallpox. N.p., n.d. Web. 07 Feb. 2013.
<http://timelines.tv/smPox/more/spread2.html>.
"My Map Gallery." MyWeb. N.p., n.d. Web. 07 Feb. 2013.
<http://myweb.unomaha.edu/~qbutler/gallery.html>.
"Spartacus Educational." Spartacus Educational. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Feb. 2013.
<http://www.spartacus.schoolnet.co.uk/Sequiano.htm>.
"Home." Home. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Feb. 2013.
<http://www.ucalgary.ca/applied_history/tutor/migrations/four5.html>.
Wiki. N.p., 27 Dec. 2007. Web. 07 Feb. 2013.
Cassie Jones." History100slaverys Blog. N.p., n.d. Web. 07 Feb. 2013.
rans-Saharan Trade." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 02 Apr. 2013. Web. 07 Feb. 2013.
"The
Interesting Narrative of the Life of Olaudah Equiano, or Gustavus Vassa, the African. Written by
Himself. Vol. I." Documenting the American South. N.p., n.d. Web.
<http://docsouth.unc.edu/neh/equiano1/summary.html>.
"European
Exploration and Colonization, Page 13." American History. N.p., n.d. Web. 07 Feb. 2013. <http://aventalearning.com/content168staging/2008AmHistA/unit1/html/section_4_page_13.html>.
"Medicine through Time - Smallpox." Smallpox. N.p., n.d. Web. 07 Feb. 2013.
<http://timelines.tv/smPox/more/spread2.html>.
"My Map Gallery." MyWeb. N.p., n.d. Web. 07 Feb. 2013.
<http://myweb.unomaha.edu/~qbutler/gallery.html>.
"Spartacus Educational." Spartacus Educational. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Feb. 2013.
<http://www.spartacus.schoolnet.co.uk/Sequiano.htm>.
"Home." Home. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Feb. 2013.
<http://www.ucalgary.ca/applied_history/tutor/migrations/four5.html>.