Globalization and Latin America
Rea Maci
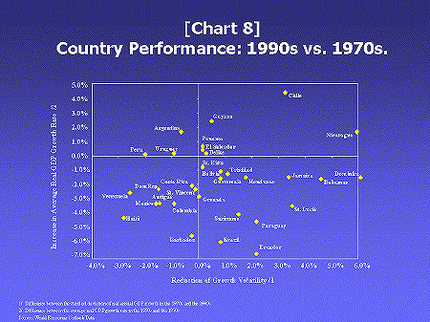
The 1980s and 1990s have been decades of instability and slow growth for most of the Latin American region. In recent years globalization has affected different regions of Latin America in different ways. Globalization marks an extraordinary triumph of capitalism relying on the global mobility of all factors of production along with the agreement of governments not to interfere with the markets’ share of resources. As a result of the debt crisis of the 1980s the Latin American nations have reopened their economies to extensive trade with the rest of the world. At first with skepticism and then with more ease the region has taken to the liberal ideology within the frame of the world economy. However as a consequence of these liberal ideas and policies, Latin American regions have become tied to the market economies and more dependent and closely mixed into the global economy as exporters of their natural resources and importers of manufactures. Exports are being promoted and foreign investors have been invited to buy state enterprises while all free trade agreements are enthusiastically promoted. Ironically enough the more the region integrates into the post Cold War era of economic globalization which includes free market and fierce competition for the upper hand market control, the more fear of being left out without any rational economic alternatives lingers. The effects of globalization have not been very kind or orderly to Latin America. With some exceptions such as Chile, Costa Rica and northern Mexico the openness of their economy has increased the social disintegration within the inside societies. “The new mobility of international capital has made Latin American economies more dependent, increasing their vulnerabilities to change in world capital markets and reducing their policy to autonomy (O’Toole 1999, 453). Therefore, the rising of a new populist left in Latin America in places such as Ecuador, Venezuela and Bolivia can be understood as political reactions to globalization. In the process of globalization regionalism is also emerging as a strong force. Because regionalism is another chapter of globalization it can be understood by the idea that, by helping national economies become more competitive in the world market, regional integration could lead to multilateral cooperation on a global scale. And then the process of regional integration can be interpreted as part of the global economic order. In addition “globalization is be deepening the region’s traditional role as a source of raw materials and primary products by creating important new markets and export opportunities in countries such as China. At the same time, technological development and the availability of global investments have made new types of economic activity possible in the region, like the launching of high-tech and services projects in small countries such as Costa Rica and Panama” (O’Toole 2007, 453-454). In conclusion globalization has been both a driving force for the Latin American economy to compete with the rest of the world and at the same time it has also hindered some regions
Information Sources:
http://www.eclac.org/publicaciones/xml/5/21325/lcl2236i.pdf
http://www.historyworld.net/wrldhis/plaintexthistories.asp?paragraphid=npb
http://marie-mckeown.hubpages.com/hub/Latin-America-Political-Economic-Force
http://www.eclac.org/publicaciones/xml/5/21325/lcl2236i.pdf
http://www.historyworld.net/wrldhis/plaintexthistories.asp?paragraphid=npb
http://marie-mckeown.hubpages.com/hub/Latin-America-Political-Economic-Force