AGMSPRITE
5.3.2c by Megan White
Geography, Economy, and Technology
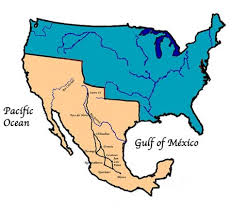
Mexico Before
In 1848, the Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo was signed in which Mexico sold more than half of its territory, including present day Arizona, Colorado, Nevada, Utah, New Mexico and Texas. The selling of these lands caused dramatic effects on Mexico, due to the lands possessing rich soil and mining opportunities. By selling these lands, Mexico lost a lot of income and land, causing them to have a smaller food source, places for work, and in turn a smaller population. A smaller population would lead to additional harmful effects, such as loss of innovations.
Political

Benito Juarez, first Mexican president
As stated previously in "The Effects of the Mexican Revolution", Mexico had many years of struggling attempting to settle on a form of government. Eventually, two main political groups formed: the Conservatives and the Liberals. Liberals wished the government would closely resemble that of the United States, whereas Conservatives wanted the government to be similar to Spain's. This political diffusion would lead to further repercussions because there would constantly be disagreements and little could get done in a short amount of time.
Agriculture and Social

Current poverty rates (2005)
The war had a harsh toll on the land causes much of it to be infertile. Most of the land that survived were in the territories Mexico was forced to give away. Virtually Mexico had to import much of their food because most food grown in Mexico was either in short supply or unsanitary. This food shortage lead to an increase in poverty. The social aspects in Mexico also were effected by the war because of the outrageous number of deaths, causing an exponential decrease in population and having mental effects on those who survived.To this day, Mexico has a high poverty rate.
Military

After the war ended, much of Mexico's military members had been killed. In addition, the struggle to determine a government lead to Mexico failing to repay debt to France, England, and Spain. Soon, all three nations came to Mexico and forced Mexico to repay their debt. Mexico had a very small military in terms of numbers and could not hold off the French, in particular, and eventually had to pay the debts. Mexico has yet to rebuild their military.
Bibliography
"Mexican War of Independence." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 25 Mar. 2013. Web. 26 Mar. 2013.
"Mexican War of Independence Begins." History.com. A&E Television Networks, n.d. Web. 20 Mar. 2013.
"War and Battle Directory." History Curriculum Homeschool. N.p., n.d. Web. 21 Mar. 2013.
"World Map." Map of Spain and Portugal the Peninsular War. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Mar. 2013.
"A Forgotten History of Democratic Institutions in Mexico and Peru." UCLA International Institute. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Mar. 2013.
"HIS-Mexico - 1810 CE to 1910 CE by Paul." HIS-Mexico - 1810 CE to 1910 CE by Paul. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Mar. 2013.
Minster, Christopher. "The Mexican Revolution." About.com Latin American History. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Mar. 2013."Mexico after Independence." Embajada De Mexico En Estados Unidos. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Mar. 2013. <http://embamex.sre.gob.mx/eua/index.php/en/meetmex/508-mexican-history?>.
"Mexican War of Independence Begins." History.com. A&E Television Networks, n.d. Web. 20 Mar. 2013.
"War and Battle Directory." History Curriculum Homeschool. N.p., n.d. Web. 21 Mar. 2013.
"World Map." Map of Spain and Portugal the Peninsular War. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Mar. 2013.
"A Forgotten History of Democratic Institutions in Mexico and Peru." UCLA International Institute. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Mar. 2013.
"HIS-Mexico - 1810 CE to 1910 CE by Paul." HIS-Mexico - 1810 CE to 1910 CE by Paul. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Mar. 2013.
Minster, Christopher. "The Mexican Revolution." About.com Latin American History. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Mar. 2013."Mexico after Independence." Embajada De Mexico En Estados Unidos. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Mar. 2013. <http://embamex.sre.gob.mx/eua/index.php/en/meetmex/508-mexican-history?>.
