AGMSPRITE
Pete Dauphin & Britney Spindler
Art & Architecture
n/a
Geography
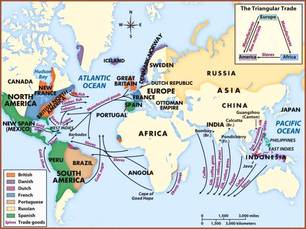
Travelers and traders were able to effectively navigate geography.
Technological innovations in transoceanic trade and travel created new interactions with geography. Developments in the Europe’s shipbuilding techniques, the lateen sail, magnetic compass, and the sternpost rudder from China allowed sailors to efficiently travel the ocean. The ability to successfully navigate the ocean lead Europeans to geographically unfamiliar areas like the Americas and Western Africa. Europe was able to conquer the Americas and geographically expand their empire.
Military

An artist's rendering of a Spaniard wielding the arquebus.
Innovative tools used in transoceanic trade and travel assisted Spanish in conquering the parts of the Americas and gaining military power. Expanding on gunpowder technology from China the Spanish were able to create more advanced weapons, like the Arquebus. Their ability to navigate the oceans and get to the Americas allowed Europeans to spread their power. Their advanced weapons assisted the Europeans in conquering the Americas. Advanced gun technology made the Europeans militaristically more powerful than the Middle East and Asia.
Society

Black people were treated as commodities.
Society was heavily altered by the innovations related to transoceanic trade and travel. A significant change in society was the use of Africans as slaves. The new technology allowed access to the West coast of Africa to easier. Although, the idea of slavery wasn't new a class of people with dark skin who did free labor was. The societies in Africa were altered because they were now being sold to Europeans and living without freedom. The ability of transoceanic trade and travel spawned interactions between people of many different cultures altering societies. The Europeans altered the Native societies in the Americas by conquering their lands and depleting their populations with foreign disease.
Politics
n/a
Religion
Advancement in technology and tools which allowed for the transoceanic trade to begin also allowed for the beginnings of colonialism and religious conquest. In this way, religion changed massively. Missionaries travelled along with traders and gained wealth and new converts. In the Americas, especially South America, religious conversion was very successful. This was primarily due to the fact that there was little written religion with which to combat Christianity (additionally, people in the americas believed that successful european conquest was a symbol
of the death of their own gods). When Europeans weren't slaying non-converts, they were creating a sort of religious patois. Oftentimes native religions would combine with Christianity. Local rituals would survive and christian figures (saints, etc) would take on the duties of traditional deities. Beyond that, Europeans were settling in the Americas to escape religious persecution and find new places in which to practice freely. Although Europeans pursued religious conquest in Asia, it did not take well primarily because Christianity was very different to Asian religions such as Buddhism, Hinduism, and Confucianism, which oftentimes focused on reincarnation and strict social hierarchy. Additionally, Asian religions were based in literature and sacred texts which are much harder to overtake than verbal religion.
of the death of their own gods). When Europeans weren't slaying non-converts, they were creating a sort of religious patois. Oftentimes native religions would combine with Christianity. Local rituals would survive and christian figures (saints, etc) would take on the duties of traditional deities. Beyond that, Europeans were settling in the Americas to escape religious persecution and find new places in which to practice freely. Although Europeans pursued religious conquest in Asia, it did not take well primarily because Christianity was very different to Asian religions such as Buddhism, Hinduism, and Confucianism, which oftentimes focused on reincarnation and strict social hierarchy. Additionally, Asian religions were based in literature and sacred texts which are much harder to overtake than verbal religion.
Intellect
A result of transoceanic trade was that ideas were able to spread more quickly. Although, transoceanic trade was not the genesis of racism it was perpetuated it. The European traders viewing Africans as a commodity perpetuated the idea of racism to Europeans. The ability to navigate oceans lead to the spread of technological ideas and Christianity on different continents.
Technology

The prompt focuses on the development of new tools in order to advance transoceanic trade. See the Case Study for more details.
In addition to the compass, other technologies include the sextant and the astrolabe. The sextant was invented in the early 1700s and is a navigational tool. It is a simple tool which uses mirrors and reflection to find the angle of celestial bodies in relation to the horizon. Using that information to navigate and find your location is a slightly more challenging process which involves complex calculations, charts, and extensive knowledge of the earth in relation to other celestial bodies.
This is just one example of the way technologies advanced and developed to aid navigation and travel.
The image to the right is a sextant used for navigation.
In addition to the compass, other technologies include the sextant and the astrolabe. The sextant was invented in the early 1700s and is a navigational tool. It is a simple tool which uses mirrors and reflection to find the angle of celestial bodies in relation to the horizon. Using that information to navigate and find your location is a slightly more challenging process which involves complex calculations, charts, and extensive knowledge of the earth in relation to other celestial bodies.
This is just one example of the way technologies advanced and developed to aid navigation and travel.
The image to the right is a sextant used for navigation.
Economy
The transoceanic trade revitalized Europe's economy in a new way. Europe was forced to expand outside of its continental region in order to find new ways to compete with India and China in trade. Europeans took control in the Americas and the Philippines, and also colonized port cities throughout coastal Asia. These ports and colonies began to level out the massive trade deficit Europe had to Asia. The English and the Dutch created their own trade empires in Asia while the Spanish colonized the Philippines and the Portuguese controlled much of the Indian Ocean. They were able to control their own commerce without relying on Middle Eastern traders to act as a go-between. Europe also had new access to the Americas and was able to take advantage of the resources there, too. 80% of the world's silver was at one time found in Spanish America, and the European fur trade flourished because of the abundance of fur-bearing animals in the Americas. Furthermore, Europeans were also able to trade with Native Americans They traded so much that Native Americans in fact became dependent on European goods such as iron tools, gunpowder, and textiles. The expansion of trade and the growth of the world economy due to the spread of transoceanic trade was massive.
Works Cited
Compton, Marc. Lecture.
Equiano, Olaudah. "Excerpts from Slave Narratives - Chapter 3." Excerpts from Slave Narratives - Chapter 3. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Feb. 2013.
"European Voyages of Exploration: Shipbuilding." European Voyages of Exploration: Shipbuilding. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Feb. 2013.
"How to Use a Sextant." Robin's Dockside Shop Online. Robin's Dockside Shop, n.d. Web. 05 Feb. 2013. <http://www.robinsdocksideshop.com/how_to_use_a_sextant.htm>.
Slave Auction Ad.jpg. Digital image. Wikipedia. N.p., n.d. Web.
"Spanish Soldier Aiming an Arquebus in the New World, 16th Century Giclee Print." , Images, Pictures, Spanish Soldier Aiming an Arquebus in the New World, 16th Century Posters Code. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Feb. 2013.
Strayer, Robert W. Ways of the World: A Brief Global History. [S.l.]: Bedford Bks St Martin'S, 2012. Print.
Equiano, Olaudah. "Excerpts from Slave Narratives - Chapter 3." Excerpts from Slave Narratives - Chapter 3. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Feb. 2013.
"European Voyages of Exploration: Shipbuilding." European Voyages of Exploration: Shipbuilding. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Feb. 2013.
"How to Use a Sextant." Robin's Dockside Shop Online. Robin's Dockside Shop, n.d. Web. 05 Feb. 2013. <http://www.robinsdocksideshop.com/how_to_use_a_sextant.htm>.
Slave Auction Ad.jpg. Digital image. Wikipedia. N.p., n.d. Web.
"Spanish Soldier Aiming an Arquebus in the New World, 16th Century Giclee Print." , Images, Pictures, Spanish Soldier Aiming an Arquebus in the New World, 16th Century Posters Code. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Feb. 2013.
Strayer, Robert W. Ways of the World: A Brief Global History. [S.l.]: Bedford Bks St Martin'S, 2012. Print.
