AMGSPRITE
|
Religion in Cities was vital in the development of art and architecture of the second wave civilizations. On the topic of art, cities provide the surpluses to support artists and artisans. Religious institutions compiled much of the wealth and surplus food of a city. This shows why much of the art from this time is religious and why spectacular architecture, such as the Parthenon and the Pantheon, were built as temples.
|
|
Geography of cities plays an important role in the spread of religious rituals and religion. The proximity of Greece to Rome allowed for the spread of Greco-Roman polytheism throughout the Mediterranean. The actual geography of a city determined whether they could build large temples, because of the topography of the land and availability of resources. Geography also isolated some areas of the world which created safe havens for one religion. Cities are the center or religion in the ancient world.
|
|
Religion is a major part of the culture of empires in the ancient world. If a conqueror wanted to destroy a culture, he would have to destroy the religion. To destroy religion he would have to capture or destroy the cities of his enemy. Societal values were often incorporated into religious practices. Cities had more people living in them the the country so religious values can be seen more plainly. The idea that women were less than men was incorporated into the religion. Incorporated practices such as gender superiority were more common, and more strongly enforced in cities than in the countryside.
|
|
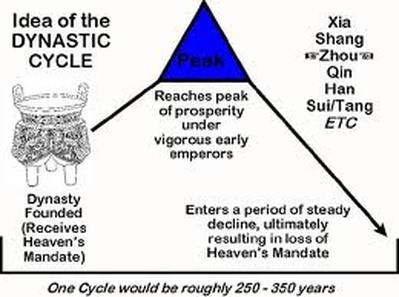
Religion has been used throughout time to gain power and manipulate people, as can be seen in China with the mandate of heaven principle. Cities were the focus of that manipulation. Priests used their ability to interpret religions and literacy to manipulate the illiterate lower classes. Religious figures stated that their temples needed sacrifices or that temple goers had donate money to be favored by the gods. The wealth and power that religion gave its priests meant that they could have unparalleled political power as they could easily manipulate the masses to do their bidding. The religion of a city dictated what types of religious rituals were practiced within its walls. In Teotihuacan human sacrifices and bloodletting were common practice. In the Roman and Persian Empires temples collected money and animals as offerings to please the gods. In India and southeast asia followers of the Buddha built monasteries in proximity to cities so that people seeking enlightenment could easily begin the path.
Religious practices had a minor effect on technological innovation in Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. The building of religious structures, and defences being the purpose of those technologies. In China, however, their prominent belief system, Confucianism, promoted learning and the answering of questions. This leads to the development of the Chinese innovation machine. The technology created by the Chinese would not be duplicated in western Eurasia until the renaissance.Confucianism, caused China to take superior advantage of its resources, led to Chinese cities being more prosperous because of advanced technology and building techniques. |
|
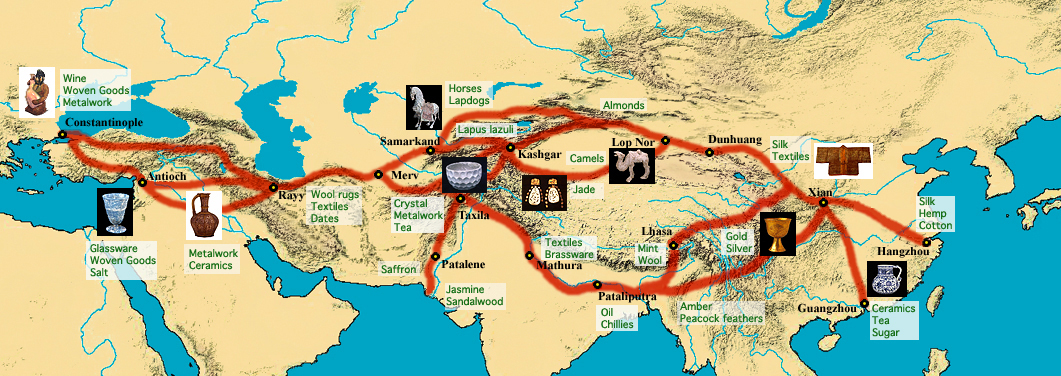
While the spread of religion depended on geography, the it was accelerated by trade routes. Buddhism got to China because of the Silk Road. Christianity spread to Rome and throughout the empire because of the empire’s large established trading web. Christianity also spread to the Axum empire in present day Ethiopia because of the trade routes on the Red Sea. Islam spreads over North Africa and Spain due to the coastal roads built by the Romans.
|