Art and Architecture
Cultural practices including traditional music can be lost and/or turned into a fusion of traditions. Globalization can trigger a state of emergency for the preservation of musical heritage. Archivists must attempt to collect, record or transcribe repertoire before melodies are assimilated or modified. Local musicians struggle for authenticity and to preserve local musical traditions. Globalization can lead performers to discard traditional instruments.
Geography
Culture of today is still linked keenly to geography. While many countries are succumbing to Westernization, the very name of this cultural movement shows culture's geographic roots. Until the day that all of mankind views themselves as being of a single unified land known as Earth, it should be safe to assume that geography will be present concerning cultural matters. The concept of Globalization however has made geography less of and infringing factor of global competition with advances such as the internet the global field of competition has become more open and less reliant of pre-disposition of geographical location.
Military
Military has been one way in which globalization has been facilitated. It is also a way for ideas from cultures to be mixed whether the people would like it to or not. Military dominance increasingly works in close tandem with economic globalization, privatization and the drive for corporate profit. This basic understanding is essential for paving the road to a powerful united worldwide resistance movement. Post world war two
Social
Historically, social globalization has involved the continuous dispersion of ideals and religious beliefs, whether civilly or by force. Most importantly, though, it is marked by the increase in association among people from separate parts of the world. This is often countered by a diminished affinity between people in the same region. Thus people lose the sense of a national identity, which is one of the criticisms of globalization.
Political
Globalization and culture have spread many new political idea's as well. The idea of democracy has spread throughout the world as people look to gain their own freedoms. As a response to globalization, some countries have embraced isolationist policies. For example, the North Korean government makes it very difficult for foreigners to enter the country and strictly monitors their activities when they do. Aid workers are subject to considerable scrutiny and excluded from places and regions the government does not wish them to enter.
Religion
Religious movements were among the earliest cultural forces to globalize, spread by force, migration, evangelists, imperialists and traders.Christianity, Islam, Buddhism and more recently sects such as Mormonism have taken root and influenced endemic cultures in places far from their origins. Globalization promotes a lot of material wealth and some religions assert materialism interferes with connection between the individual and the divine, or that it is inherently an immoral lifestyle. So that is why many religions disapprove of globalization.
Intelect
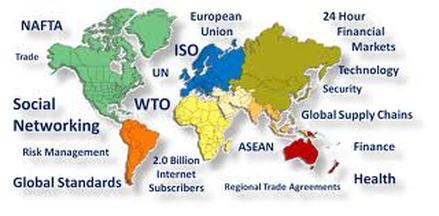
There were many intellectual developments, but it was the rapid technological developments of the 20th century that accelerated the process considerably, and which really caused people to begin contemplating globalization as a broad concept. Decade by decade, telephones, radio, jet air travel, and television media spread information around the world with increasing efficiency. By the end of the century, the Internet had made it possible for ordinary people on opposite sides of the Earth to connect instantly and cheaply, whether for the purpose of conducting business or for personal communication. In the 1990s, the growth of low cost communication networks cut the cost of communicating between different countries. More work can be performed using a computer without regard to location. This included accounting, software development, and engineering design.
Technological
Technology and cheap access to energy have altered the way the world does business, by reducing the costs of certain types of business-to-business transactions. These reduced transaction costs, driven by changes in government policies and improved communications infrastructure, have led to a wide array of business practices referred to as globalization. Technology has had a profound affect on the speed at which globalization has occurred At first when innovation was slow and things such as the printing press were introduced then globalization began to pick up. Then with the advent of the industrial revolution globalization increased to another level.
Economic
Globalization has led to the interdependence of major economies across the world. exponentially increased global trade of: technology, services, human and physical capital have created a global marketplace, that has even out the playing field for individuals from lesser developed nations with weaker economies. Current globalization trends can be largely accounted for by developed economies integrating with less developed economies, by means of foreign direct investment, the reduction of trade barriers as well as other economic reforms and, in many cases,immigration. The start of Economic globalization can be tracked back to the Bretton woods conference of 1944.
Works Cited
http://www.historyhaven.com/APWH/unit%205/GLOBALIZATION%20OF%20SCIENCE.htm
http://www.hugo-international.org/blog/?p=317
http://worldsci.net
http://www.globalization101.org/information-technology/
http://www.asis.org/Bulletin/Jun-99/globalization_and_information_.html
http://mediaif.emu.edu.tr/pages/atabek/GCS7.html
http://www.hugo-international.org/blog/?p=317
http://worldsci.net
http://www.globalization101.org/information-technology/
http://www.asis.org/Bulletin/Jun-99/globalization_and_information_.html
http://mediaif.emu.edu.tr/pages/atabek/GCS7.html